
In radio communication, skywave communication is a technique in which radio waves are transmitted at an angle into the sky and reflected back to Earth by layers of charged particles in the ionosphere. The amount of ripple in this class of filter can be set by the designer to any desired value, hence the ratio used could be any value. For instance, in the case of the Chebyshev filter it is usual to define the cutoff frequency as the point after the last peak in the frequency response at which the level has fallen to the design value of the passband ripple. Sometimes other ratios are more convenient than the 3 dB point. Where s is the s-plane variable, ω is angular frequency and j is the imaginary unit. As a voltage ratio this is a fall to 1 / 2 ≈ 0.707
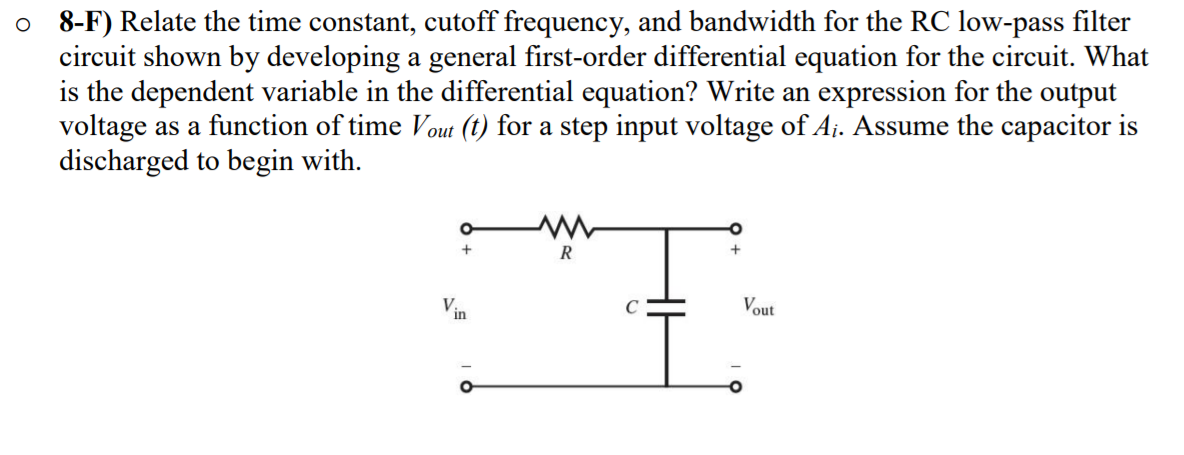
Most frequently this proportion is one half the passband power, also referred to as the 3 dB point since a fall of 3 dB corresponds approximately to half power. In electronics, cutoff frequency or corner frequency is the frequency either above or below which the power output of a circuit, such as a line, amplifier, or electronic filter has fallen to a given proportion of the power in the passband.

Typically in electronic systems such as filters and communication channels, cutoff frequency applies to an edge in a lowpass, highpass, bandpass, or band-stop characteristic – a frequency characterizing a boundary between a passband and a stopband. In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced ( attenuated or reflected) rather than passing through. A Bode plot of the Butterworth filter's frequency response, with corner frequency labeled


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
